Big Data is one of the most prevalent fields of research and knowledge that has generated high impacts in the digital transformation process of organizations in recent years. The main goal of Big Data is to improve work processes by analysing and interpreting large data. It is important to know how big data works, its advantages, challenges and tools to ensure success in business.
Big data is defined by five Vs: volume, velocity, variety, veracity and value. The volume is the amount of data that can be stored and managed; velocity is the speed of calculation required for querying the data relative to the rate of data change; the variety measures the number of different data formats( e.g. text, audio, video). Veracity refers to data messiness or trustworthiness; and value is the importance given to accessing these data by companies/ entities.
The process of working with a large amount of data offers many advantages, because it enables us to be more rigorous in our decisions. At the same time, however, its increase in volume must also be accompanied by an improvement in the quality of the data. Otherwise, several challenges arise in different dimensions.
What is Big Data?
Before we learn about big data management, we should first know what big data itself is. The common definition of big data comes from the concept of three V: Volume, Velocity, and Variety.
- Volume: Large amounts of data, ranging from terabyte to zettabyte data sets.
- Velocity: Large amounts of data from high refresh rate transactions resulting in high speed data streams, and the time to act on these data streams is often very short.
- Variety: Data come from a variety of sources, both internal and external. Also, data can come in different formats such as transaction and log data from different applications, structured data such as database table, semi- structured data such as XML data, unstructured data such as text, images, audio statement, video streams etc.
According to Gartner (2012),
Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and/or high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing that enable enhanced insight, decision making, and process automation.
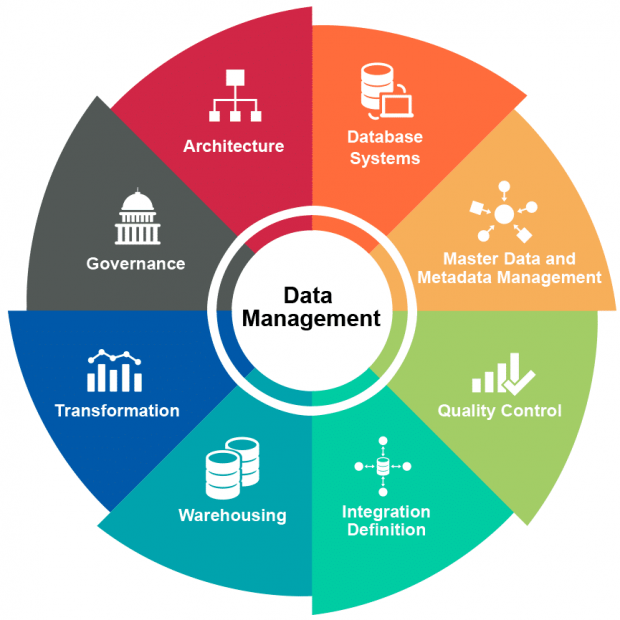
What is Big Data Management?
Big data management is the organization, administration and control of large quantities of structured and unstructured data. Big data management aims to ensure a high level of data quality and accessibility for applications in business intelligence and Big Data Analytics. Big data management strategies are used by companies, government agencies and other organizations to help them cope with rapidly growing data pools, typically involving many terabytes or even petabytes of information saved in a variety of file formats. Effective Big Data management helps companies to locate valuable information from a variety of sources, including call details, system logs and social media sites, in large sets of unstructured data and semi- structured data.
Benefits of Big Data
- At the technological level, the handling of massive data volumes, accessible and accurate data, the scalability and the integration of structured and unstructured data can be beneficial.
- The computer models and the high volume processing of data have led to the development of storage systems with high performance, high efficiency and scalability.
- One of the most obvious advantages is the financial benefits offered by big data. Large quantities of storage space at lower prices are available.
- Companies can achieve a wide range of competitive advantages: new products and services, new business models, consumer behaviour insights, increasing customer satisfaction, increasing customer loyalty, increasing registration, customer experience personalization, holistic organizational vision and data- driven marketing.
Challenges of Big Data
- Storage and analysis of data is a major concern in the management of big data. At this level, there are challenges with regard to hardware infrastructure, high- dimensional data, data integration, data quality, data provenance and real- time data.
- Scalability and data visualization is another problem of big data.
- The biggest security drawbacks are the lack of authentication mechanisms and the lack of access to information via secured channels, such as the use of encryption.
Key Points
- Big data management is the organization, administration and control of large quantities of structured and unstructured data.
- Big data management aims to ensure a high level of data quality and accessibility for applications in business intelligence and Big Data Analytics.
- The benefits offered by Big Data can be categorised into three domains:
- technology
- financial
- competitive advantage.
- The challenges found in Big Data management include:
- data storage and analysis
- scalability and data visualization
- knowledge discovery
- information security
- human resources and manpower
- appearance of new technologies
- The big data tools are categorized into three groups:
- computing tools
- storage tools
- support technologies.








